 1. Getting started with MSC/ PATRAN:
Access MSC/PATRAN, run a Session File, move, resize and iconify windows and forms, then become familiar with Screen Picking and the on-line help utility.
1. Getting started with MSC/ PATRAN:
Access MSC/PATRAN, run a Session File, move, resize and iconify windows and forms, then become familiar with Screen Picking and the on-line help utility.Computer-Based Modeling for Design and Analysis with MSC/PATRAN-PAT301
 1. Getting started with MSC/ PATRAN:
Access MSC/PATRAN, run a Session File, move, resize and iconify windows and forms, then become familiar with Screen Picking and the on-line help utility.
1. Getting started with MSC/ PATRAN:
Access MSC/PATRAN, run a Session File, move, resize and iconify windows and forms, then become familiar with Screen Picking and the on-line help utility.
 2. Importing Geometry from an IGES file:
Import geometry from an IGES file, create a solid from curves and surfaces then Tet mesh the solid.
2. Importing Geometry from an IGES file:
Import geometry from an IGES file, create a solid from curves and surfaces then Tet mesh the solid.
 3. Geometry Model of a Connecting Rod:
Import geometry from an IGES file and create geometry in MSC/PATRAN (Phase I).
3. Geometry Model of a Connecting Rod:
Import geometry from an IGES file and create geometry in MSC/PATRAN (Phase I).
 4. Geometry Model of a 3-D Clevis:
Create a new database, create geometry and change the graphics display.
4. Geometry Model of a 3-D Clevis:
Create a new database, create geometry and change the graphics display.
 5. Views of a 3-D Clevis:
Become familiar with different view options then create and modify the z-axis and arbitrary clipping planes.
5. Views of a 3-D Clevis:
Become familiar with different view options then create and modify the z-axis and arbitrary clipping planes.
 6. Display Exercise:
Become familiar with various display options, create and use your own named attribute sets and add text to displays.
6. Display Exercise:
Become familiar with various display options, create and use your own named attribute sets and add text to displays.
 7. 1st Finite Element Model of a 3-D Clevis:
Apply a nonuniform mesh seed near a critical location of the 3-D Clevis model then apply a global mesh to the seeded model.
7. 1st Finite Element Model of a 3-D Clevis:
Apply a nonuniform mesh seed near a critical location of the 3-D Clevis model then apply a global mesh to the seeded model.
 8. 2nd Finite Element Model of a 3-D Clevis:
Use Chaining to create a Curve, create a Trimmed Surface, sweep a Surface Mesh to create Solid elements then use the Finite Elements Transform option.
8. 2nd Finite Element Model of a 3-D Clevis:
Use Chaining to create a Curve, create a Trimmed Surface, sweep a Surface Mesh to create Solid elements then use the Finite Elements Transform option.
 9. Verification and Property Assignment:
Prepare previous model for analysis by eliminating duplicate nodes and verifying element attributes then apply material and element properties.
9. Verification and Property Assignment:
Prepare previous model for analysis by eliminating duplicate nodes and verifying element attributes then apply material and element properties.
 10. Spatial And Temporal Variation of Loads:
Model a simple flat plate with spatially and temporally varying applied loads.
10. Spatial And Temporal Variation of Loads:
Model a simple flat plate with spatially and temporally varying applied loads.
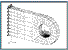 11. Loads and Boundary Conditions on a 3-D Clevis:
Apply constraints to your 3-D Clevis model then create and apply a
Field
to describe a spatially varying load.
11. Loads and Boundary Conditions on a 3-D Clevis:
Apply constraints to your 3-D Clevis model then create and apply a
Field
to describe a spatially varying load.
 12. Material Property Definition:
Create a material that has temperature dependent properties using fields wile using steps that are necessary to create almost any material definition in MSC/PATRAN.
12. Material Property Definition:
Create a material that has temperature dependent properties using fields wile using steps that are necessary to create almost any material definition in MSC/PATRAN.
 12a. Obtaining Material Properties Using the Materials Selector:
Select a material using the Materials Selector and apply it to a plate.
12a. Obtaining Material Properties Using the Materials Selector:
Select a material using the Materials Selector and apply it to a plate.
 13. Spatial Variation of Physical Properties:
Model a circular plate which has a hole at its center and has variations of its physical properties as a function of spatial coordinates.
13. Spatial Variation of Physical Properties:
Model a circular plate which has a hole at its center and has variations of its physical properties as a function of spatial coordinates.
 14. Analysis Set-up of a Static Analysis:
Review all the steps necessary to build an analysis model and understand how to setup a static analysis with MSC/PATRAN for MSC/NASTRAN.
14. Analysis Set-up of a Static Analysis:
Review all the steps necessary to build an analysis model and understand how to setup a static analysis with MSC/PATRAN for MSC/NASTRAN.
 15. Using Groups and Lists:
Build a finite element model that includes element properties and boundary conditions, use lists to identify parts of the model with specified attributes and explore the Group Display mode.
15. Using Groups and Lists:
Build a finite element model that includes element properties and boundary conditions, use lists to identify parts of the model with specified attributes and explore the Group Display mode.
 16. Post Processing of Displacement Results:
Examine the deformation of the MSC/NASTRAN model to evaluate the validity of the assumptions made in the creation of the mesh density and selection of element type.Use the “Basic” and “Advanced” results in post-processing forms.
16. Post Processing of Displacement Results:
Examine the deformation of the MSC/NASTRAN model to evaluate the validity of the assumptions made in the creation of the mesh density and selection of element type.Use the “Basic” and “Advanced” results in post-processing forms.
 17. Post Processing of Stress Results With Results:
To post-process stress results from MSC/NASTRAN and use MSC/PATRAN to create fill and fringe plots to determine if the analyzed part will meet a customer-defined criteria or whether the part needs to be re-designed and re-analyzed.
17. Post Processing of Stress Results With Results:
To post-process stress results from MSC/NASTRAN and use MSC/PATRAN to create fill and fringe plots to determine if the analyzed part will meet a customer-defined criteria or whether the part needs to be re-designed and re-analyzed.
 18. Post-Processing Transient Response With Results:
For a simple plate animate the Transient Structural response and create a x-y plots of the structural displacement versus time.
18. Post-Processing Transient Response With Results:
For a simple plate animate the Transient Structural response and create a x-y plots of the structural displacement versus time.
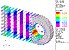 19. Post Processing with Insight:
Create various Insight tools to display the results of analysis from a previous Clevis model.
19. Post Processing with Insight:
Create various Insight tools to display the results of analysis from a previous Clevis model.
 20. Transient and Modal Animation:
Introduction of insight animation tools, perform transient animation and perform standard and quick modal animation.
20. Transient and Modal Animation:
Introduction of insight animation tools, perform transient animation and perform standard and quick modal animation.
 21. Post-Processing of Time-Dependent Results:
Examine the results of a transient thermal analysis from MSC/THERMAL, create Fringe and X-Y Plots then perform a transient animation.
21. Post-Processing of Time-Dependent Results:
Examine the results of a transient thermal analysis from MSC/THERMAL, create Fringe and X-Y Plots then perform a transient animation.
 22. Importing a PATRAN 2.5 Model into P3:
Read a PATRAN 2.5 neutral file into P3, import PATRAN 2.5 result files into your P3 database and work with multiple load cases.
22. Importing a PATRAN 2.5 Model into P3:
Read a PATRAN 2.5 neutral file into P3, import PATRAN 2.5 result files into your P3 database and work with multiple load cases.