 1. Keymapping PCL Functions:
Learn how to map PCL commands into a selected key, and use session file to create a PCL function.
1. Keymapping PCL Functions:
Learn how to map PCL commands into a selected key, and use session file to create a PCL function.MSC/PATRAN for Advanced Users-PAT302
 1. Keymapping PCL Functions:
Learn how to map PCL commands into a selected key, and use session file to create a PCL function.
1. Keymapping PCL Functions:
Learn how to map PCL commands into a selected key, and use session file to create a PCL function.
 2. Merging Databases:
Using separate databases to model the part is illustrated in this exercise. The purpose of this exercise is to become aware of how MSC/PATRAN resolves conflicts when merging two databases.
2. Merging Databases:
Using separate databases to model the part is illustrated in this exercise. The purpose of this exercise is to become aware of how MSC/PATRAN resolves conflicts when merging two databases.
 3. Adding an Icon to Quick Pick:
Create a PCL Class which contains a PCL Built-in function to shrink finite elements. Create an icon to invoke the PCL function in the Quick Pick.
3. Adding an Icon to Quick Pick:
Create a PCL Class which contains a PCL Built-in function to shrink finite elements. Create an icon to invoke the PCL function in the Quick Pick.
 3a. Adding an Icon to Toolbar:
Create a PCL Class which contains a PCL Built-in function to shrink finite elements. Create an icon to invoke the PCL function in the Toolbar.
3a. Adding an Icon to Toolbar:
Create a PCL Class which contains a PCL Built-in function to shrink finite elements. Create an icon to invoke the PCL function in the Toolbar.
 4. Composite Trimmed Surfaces:
Create composite surfaces to fix disjointed surfaces of an imported drawing, and construct a single, fluid, consistent mesh which can be used for purposes of analysis.
4. Composite Trimmed Surfaces:
Create composite surfaces to fix disjointed surfaces of an imported drawing, and construct a single, fluid, consistent mesh which can be used for purposes of analysis.
 5. Geometry Construction:
Create the required 2-D geometry for a 3-D model.
5. Geometry Construction:
Create the required 2-D geometry for a 3-D model.
 6. Imported Geometry Cleaning:
Learn to remove unnecessary geometric details in an imported drawing.
6. Imported Geometry Cleaning:
Learn to remove unnecessary geometric details in an imported drawing.
 7. Generating a Hex Mesh Using Vector Sweep:
Show an alternative to create solid finite elements from solid geometry.
7. Generating a Hex Mesh Using Vector Sweep:
Show an alternative to create solid finite elements from solid geometry.
 8. Preparing Geometry for a Hex Mesh:
Learn to use the method of Decomposing to create new surfaces. Decomposition of the CAD geometry is required when IsoMeshing a solid.
8. Preparing Geometry for a Hex Mesh:
Learn to use the method of Decomposing to create new surfaces. Decomposition of the CAD geometry is required when IsoMeshing a solid.
 9. Finite Element Model:
Learn an alternative to create your finite element model by using Mesh Sweep . Mesh sweep creates elements by sweeping existing elements, therefore no supporting geometry is required.
9. Finite Element Model:
Learn an alternative to create your finite element model by using Mesh Sweep . Mesh sweep creates elements by sweeping existing elements, therefore no supporting geometry is required.
 10. Using Lists and Multi-Point Constraints:
Learn how to use Multi-Point Constraint (MPC) to connect two dissimilar elements. MPC accounts for the rotational degrees of freedom defined in the elements.
10. Using Lists and Multi-Point Constraints:
Learn how to use Multi-Point Constraint (MPC) to connect two dissimilar elements. MPC accounts for the rotational degrees of freedom defined in the elements.
 11. Mass Properties Calculations:
Import a unigraphics express file and apply mass properties to the model.
11. Mass Properties Calculations:
Import a unigraphics express file and apply mass properties to the model.
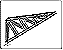 12. Freebody Analysis of a Truss:
Create the geometry for a simple truss, and perform a freebody analysis on the truss.
12. Freebody Analysis of a Truss:
Create the geometry for a simple truss, and perform a freebody analysis on the truss.
 13. Cylinder with T-Beam Stiffeners:
Learn how to create a cylinder with applied loads. Learn to use the beam library to add stiffeners to the cylinder.
13. Cylinder with T-Beam Stiffeners:
Learn how to create a cylinder with applied loads. Learn to use the beam library to add stiffeners to the cylinder.
 14. Global / Local Model using FEM Fields:
Demonstrate on how to use Global Loads Model to obtain Local Stress Model.
14. Global / Local Model using FEM Fields:
Demonstrate on how to use Global Loads Model to obtain Local Stress Model.
 15. Importing Results using a Results Template:
Create results templates that will allow you to import a set of nodal results and displacements. The template created in this exercise will allow the user to easily import a custom set of results that would otherwise not be supported.
15. Importing Results using a Results Template:
Create results templates that will allow you to import a set of nodal results and displacements. The template created in this exercise will allow the user to easily import a custom set of results that would otherwise not be supported.
 16. Projected Coordinate Systems:
Get familiar with the difference between Global and Projected-Global coordinate systems.
16. Projected Coordinate Systems:
Get familiar with the difference between Global and Projected-Global coordinate systems.
 17. Post Processing of Results:
Learn details about obtaining results.
17. Post Processing of Results:
Learn details about obtaining results.
 18. Parametrized Pipe Intersection:
Learn how to model a cylinder (pipe) of one radius intersecting a cylinder of a different radius.
18. Parametrized Pipe Intersection:
Learn how to model a cylinder (pipe) of one radius intersecting a cylinder of a different radius.
A. MSC/PATRAN Settings Listed By Category: Display the definition and location of the MSC/PATRAN commands.
B. Unix Quick Reference: Display the UNIX commands.
C. Icon and Text Editors: Useful information on various Icon Editors.